Science
Monday, May 5, 2014
Jellyfish
This post is about the science behind jellyfish stings and how it works. First off, jellyfish are not really fish, they are actually plankton. Jellyfish do not plan attacks on humans because their nervous system isn't advanced enough to do so. Their tentacles are for defense and a way to capture their prey. Jellyfish are carnivores and what they eat depends on their size. Smaller ones eat algae and zooplankton while larger ones eat crustaceans and other sea creatures. Every one of their tentacles are covered in cnidoblast cells that contain nematocysts. When a tentacle comes in contact with another object, threads inside the nematocysts uncoil, shooting out venom like darts. The venom is a neurotoxin, which paralyzes the prey. The strength of the venom depends on the species. Larger ones tend to have larger cnidoblasts that go deeper into the skin and some have more toxic venom. Be careful walking on the beach because dead jellyfish, and even the tentacles separated from the actual jellyfish can still sting.
Tuesday, April 8, 2014
Acid
Acid is a very dangerous substance, that needs to be handled with care. If the acid has a higher concentration, it can do more damage to the human body. If it is diluted, it may just make the area of contact red. Acid burns look like a regular first, second, or third degree burn. If highly burned, corrective surgery is required. Hydrofluoric acid is the most dangerous acid, and can do a lot of damage. When inside the body, it burns you from the inside out. The fluoride ions bond to the calcium in the bones, which can lead to heart failure, which is more dangerous than burns. The fluoride also clogs blood vessels and tears up tissues. Not only is the acid itself dangerous, but the fumes are as well. Always wear proper protective gear when handling any acid.
Article 1
Article 2
Photo Creds
Article 1
Article 2
Photo Creds
Thursday, March 6, 2014
Dreams
No one knows exactly why we dream. Everyone dreams but not everyone remembers them. Wether or not someone remembers them, depends on the person. On average you can have up to 4-7 dreams per night which is about 2 hours of dreaming. One theory of why we dream is that the brain sorts out everything from the day. It sorts out what is important and what is not. Another theory is that when we sleep our brain slows down and makes loose connections in our dreams. Blind people still dream. If they were born blind, their other senses are heightened, like hearing, smell, etc. People who became blind after birth still see images. When you see people in your dreams, you've seen them in person. It could simply be a random person in the crowd. In a study, scientists found that people who were learning dreamed more than people who weren't. If someone is snoring, they cannot be dreaming.
Article 1
Article 2
Article 1
Article 2
Wednesday, February 19, 2014
Chemical Changes
Chemical changes happen all around us. It can be when the leaves change, rotting food, or when things start to smell differently than how they did before. Chemical changes happen when you combine two or more substances and they transform into another substance. The new substance has new physical and chemical properties. Reactions can include ions, compounds or molecules of an element. Single reactions usually are a part of a series of reactions. If you move your arm, the muscles need sugars for energy. The sugars have to be metabolized then used in your arm.
Pic credsInfo
Pic credsInfo
Friday, January 31, 2014
Glassblowing
Glass blowing has been around for a very long time, but the techniques of glassblowing haven't advanced much. There's been new technology to help, but the overall technique is pretty much the same. Glass is an amorphous solid, or a no crystalline solid. The molecular structure is more like a liquid's, it's randomized, which is why it's transparent. In glassblowing, they use top quality sand. Regular sand from the beach has too many impurities. Sometimes they add stuff like alumina, magnesia, boron oxide and lead oxide to make it easier to blow the glass. A common type of glass used is soda lime glass. It's 72% silica, 15% soda (sodium dioxide), and 9% lime (calcium oxide). Those materials are fluxes. They lower the melting point and decrease the viscosity of the glass while it's melted. It also makes it stronger. If you add different metal oxides, it will add a color. If you put cobalt in it, it will make it blue.
Pic creds
Pic creds
Tuesday, January 14, 2014
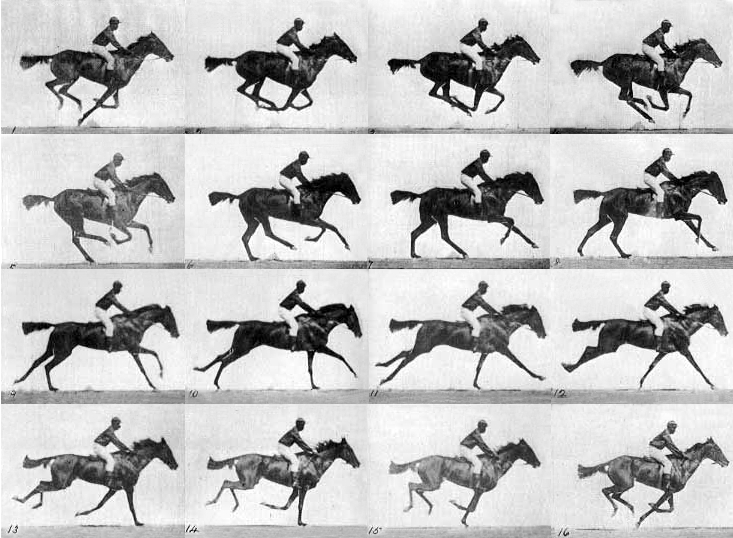
Horse Racing
Horse Racing has evolved over the years. Until the 19th century, the jockeys would sit up straight, head up, with their seat in the saddle. They thought that this let the horse go the fastest. Then they did some studies. They found out that standing up, bending forward, and moving along with the motion of the horse, enables the horse to move about 5%-7% faster. Either way, the horse still has to carry weight. Although standing up is less work for the horse, it's more for the rider. The researchers wrote, "The jockey's legs oscillate in length while transmitting a vertical force, resulting in substantial mechanical work."
Thill Pfau placed two sensors, (one on the front of the saddle to represent the horse, and another on the rider) to figure out the movements. They found that the horse's back oscillates 6 inches and the jockey moves up and down 2.3 inches. They also found that the horse is about 87% of the weight (about 1,100 pounds) and the jockey is the other 13%. The strategy of standing up while racing definitely enables the horse to move more effectively and faster.
Thill Pfau placed two sensors, (one on the front of the saddle to represent the horse, and another on the rider) to figure out the movements. They found that the horse's back oscillates 6 inches and the jockey moves up and down 2.3 inches. They also found that the horse is about 87% of the weight (about 1,100 pounds) and the jockey is the other 13%. The strategy of standing up while racing definitely enables the horse to move more effectively and faster.
Tuesday, January 7, 2014
Our Solar System
Our solar system is over 4.5 billion years old and it is one of several billion solar systems in the Milky Way Galaxy. The scientific theory of how the solar system was created was when a cloud of gas and dust was disturbed by an outside force. The cloud then compressed and the particles began to stick together by forming larger objects (the planets) and the temperature and pressure rose and a nuclear fusion began and created the sun. All of the coal, oil, gas, and wood on Earth would only keep the Sun burning for a few days. The average size of a star is about 150,000 times bigger than Earth. In the Centaurus constellation is a star named Lucy. It is a huge diamond floating in space. It weighs 10 billion trillion trillion carats and is about the size of the moon. Below is a picture of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Pic Creds
Pic Creds
Cites Used:
http://solarsystemfacts.net
http://my.chicagotribune.com/#section/-1/article/p2p-67373603/
http://hotpot.se/AmFaSciSp.htm
http://solarsystemfacts.net
http://my.chicagotribune.com/#section/-1/article/p2p-67373603/
http://hotpot.se/AmFaSciSp.htm
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)